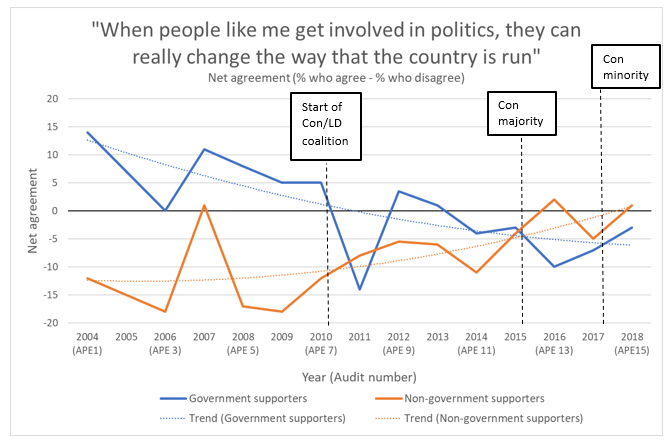
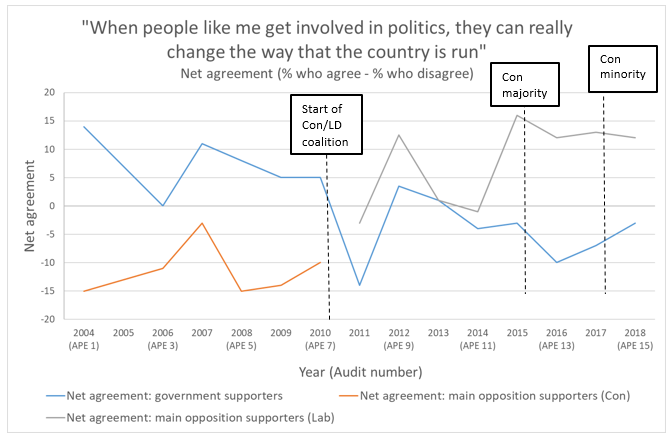
News / Jury trials under threat? The Courts and Tribunals Bill explained - Parliament Matters podcast, Episode 136
Plans to restrict the right to a jury trial have cleared their Second Reading in the Commons, but the proposals in the Courts and Tribunals Bill face growing resistance, including from Labour rebels. We discuss the legal and constitutional implications with barrister Lord Macdonald of River Glaven, examining what the reforms could mean for defendants’ rights and the criminal courts system. We also assess the passage of legislation removing hereditary Peers from Parliament, and the late compromise that eased opposition in the House of Lords. Meanwhile Sir Lindsay Hoyle clashes with the Chief Whip over delays in the division lobby, and newly released papers on Peter Mandelson’s Washington appointment raise fresh political questions. Listen and subscribe: Apple Podcasts · Spotify · Acast · YouTube · Other apps · RSS