News / Parliament Matters Bulletin: What’s coming up in Parliament this week? 2-6 March 2026
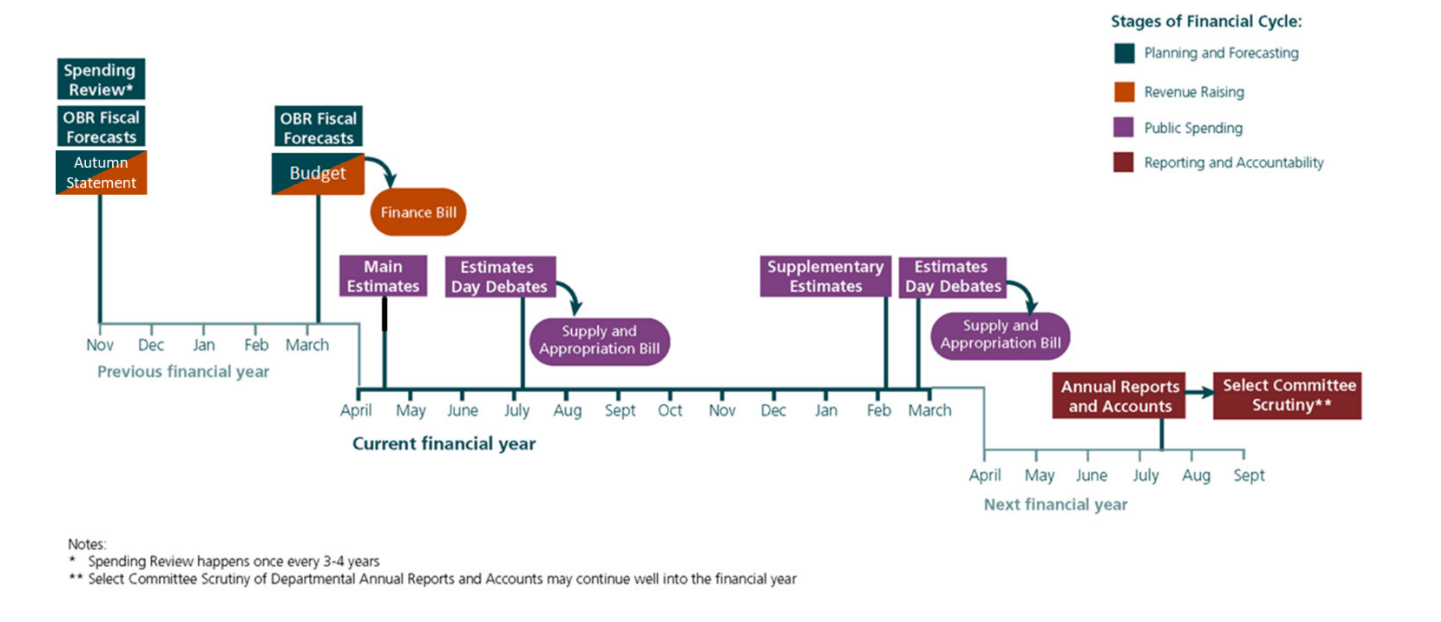
The newly elected Green MP, Hannah Spencer, will be introduced to the House of Commons. A Ministerial Statement is expected on the situation in Iran, while the Foreign Secretary faces MPs’ questions. Chancellor Rachel Reeves will deliver her Spring Statement, and MPs will consider billions of pounds in revised departmental spending through the Supplementary Estimates. The Commons will debate the Representation of the People Bill, the contribution of Commonwealth troops in the First World War, and the future of palliative care. In the Lords, Peers will scrutinise the Crime and Policing, Tobacco and Vapes, National Insurance Contributions, and English Devolution bills, as well as debate the India trade deal and International Women’s Day. Select committees will hear from Northern Ireland, Home Office and Cabinet Office ministers, military experts on the Armed Forces Bill, and Bank of England officials.